Audio stimulation🔗
2 separate audio stimulation systems are available. Each system has a different frequency and latency response.
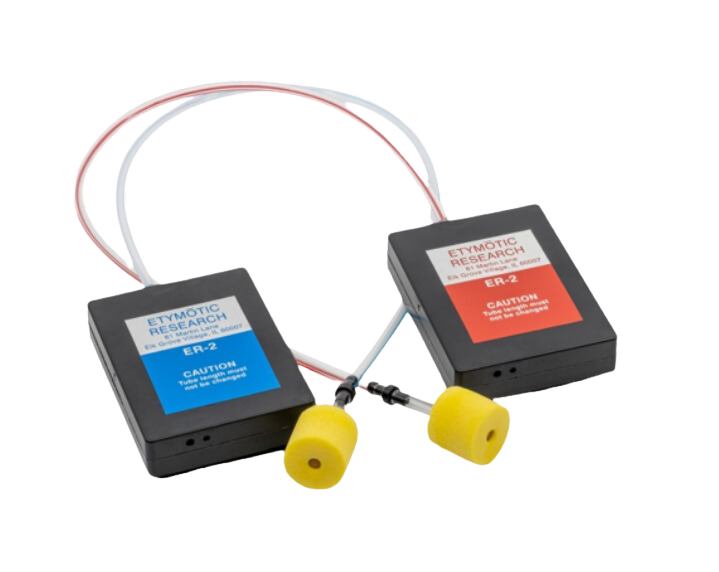
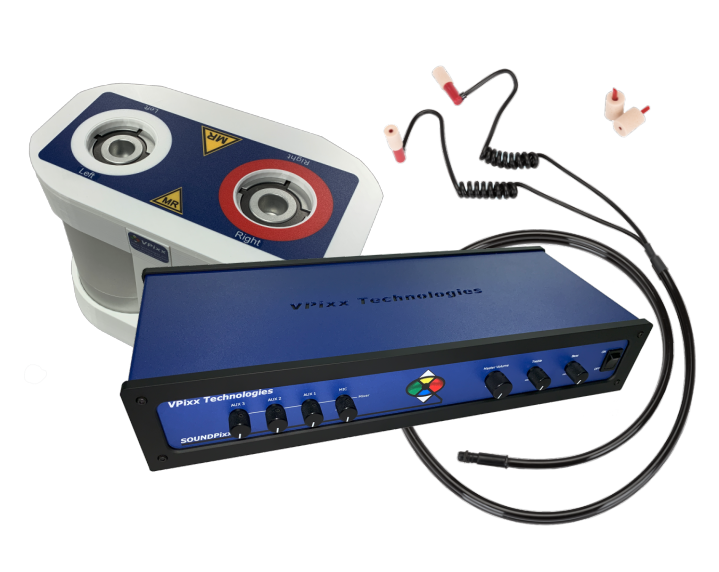



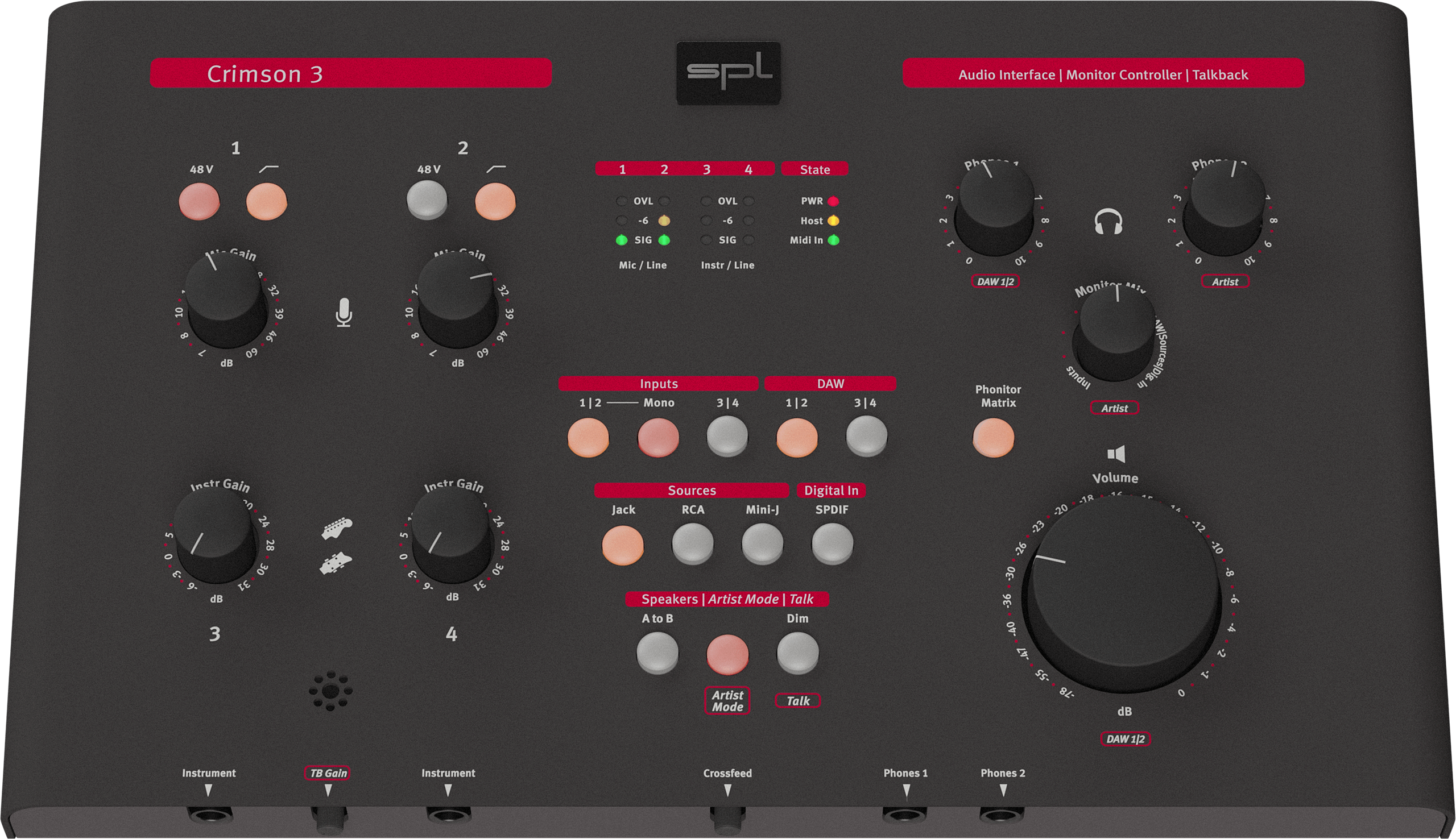
Both audio stimulation systems are connected to a USB audio interface Crimson 3 from SPL.
Select Natus TIP-300 or SoundPixx🔗
The button Speakers: A to B selects the system in use. If the button is OFF, the
speakers A corresponding to the Natus TIP-300 system
is selected. If the button is ON, the speakers B corresponding to the
SoundPixx system is selected.
Tip
If the SoundPixx is in-use, don’t forget to turn on the SoundPixx controller.
Microphone inputs 1/2🔗
The 2 microphone inputs 1 and 2 must be used without 48V phantom power and without
high-pass filter. The microphone 2 is connected to the black microphone used to speak to
the participant through the in-ear headphones. To enable the black microphone, both the
Inputs: 1|2 and Inputs: Mono button must be enabled.
Tip
The black microphone has a low volume. Don’t forget to turn the knob of input 2 to
a high value. However, don’t set it to max as it would leave a background noise. The
LEDs SIG of the microphone input 2 should remain off while the black microphone
is not in use.
Audio sources🔗
Auditory stimulation can come from 2 sources: the Chronos if E-Prime is used or
directly the computer sound (DAW). Only one of the 2 sources should be active at a time.
To use the sound from the Chronos, the button Sources: RCA must be enabled. To
use the sound from the computer, the button DAW: 1|2 must be enabled.
Note
On Windows, the computer sends sound to a single channel, DAW: 1|2. However on
Linux, it sends sound to both channels, DAW: 1|2 and DAW: 3|4, thus enabling
both yields a higher volume.
Monitoring feedback🔗
The sound from the audio stimulation system is redirected on an MEG analogical channel,
MISC 006, from the Phones 1 output. See the section
trigger to sound onset delay
and the tutorial MISC 006: a proxy measure of the audio stimuli for additional information.
2 Bose speakers are used to monitor the sound played through the audio stimulation
system. The Bose speakers are connected on Phones 2 and volume is adjusted both with
a knob on the speakers and with the knob Phones 2 on the Crimson 3.
Main volume🔗
The main volume knob affects the volume from all sources. The volume should be gradually increased from a low value up-to the desired value to prevent loud sound from deafening participants.
Trigger to sound onset delay🔗
The delay between the trigger and the sound onset is the delay between the trigger delivered to the MEG trigger system and the actual sound onset in the earphones. This delay is composed of:
(1) The hardware delay from the Crimson 3 soundcard to the audio delivery system, Natus TIP-300 or SoundPixx.
(2) The software delay due to the stimulation software (e.g. E-Prime, PsychoPy, etc..) and to the audio drivers and communication with the Crimson 3 soundcard.
Hardware delay🔗
The delay (1) from the Crimson 3 soundcard to the audio delivery system is constant
and depends only on the system in use. The optimic can
be used to record the sound output from the headset and to compare it with the sound
output from the monitoring feedback Phones 1, available on MISC 006.
Natus TIP-300 |
SoundPixx |
|
Delay |
3 ± 0 ms |
18 ± 0 ms |
The difference between both system comes partially from the amplifier/transducer, but mostly from the SoundPixx tube length of 3.6576 meters (12 feet) inducing a 10.6 ms delay due to the sound travel time.
Note
The measurement through the optimic is difficult even with sound output from the headset maximize. To improve it, shielding from environmental noise is necessary.
Moreover, the optimic is adding a source of unmeasurable delay, the delay of the measure. This delay is assumed to be constant and sub-millisecond.
Software delay🔗
The software delay depends on the audio drivers and operating system as well as the audio stimulation software used and the code associated with it. This delay should be measured for every project paradigm. This delay is unlikely to vary in time, i.e. the same program delivering auditory stimuli on the same hardware should have the same delay across different sessions. See the tutorial Precise audio presentation for a Python example using PsychoPy.
To measure the delay, replace the sound with a pure tone and record the triggers and the
sound on the MISC 006 channel through the Phones 1 monitoring feedback. This
testing setup works best with a pure tone sound at 1 kHz, downloadable below:
Do not forget to increase the sampling rate of the MEG to at least 2 kHz to correctly sample the 1 kHz pure tone sound.
In addition, we show below typical delay values when using Psychtoolbox on Matlab. We tested two priority levels: 1 and 3, and two sound device sampling rates: 44100Hz and 48000Hz.
Priority 1 |
Priority 3 |
|
44100Hz |
80.5 ± 3.3 ms |
43.3 ± 1.8 ms |
48000Hz |
75.1 ± 3.3 ms |
38.3 ± 0.9 ms |